What is Digital Transformation in Manufacturing?
Digital transformation in manufacturing is the use of technology and new methodologies to future-proof industries and create new opportunities in a more connected world.
The post-Covid world presents many challenges to manufacturers, including supply chain issues, changing market trends, and rapid advancements in new technologies. The digitalization and automation of the manufacturing industry is accelerating. This environment has also given businesses the impetus to modernize old processes and transform their practices.
The senior leadership in any business must be at the forefront of the cultural and technological changes that drive digital transformation. In a McKinsey survey on Digital Transformation in 2022, 73% of leading companies say that senior leadership must be involved in shaping the company-wide strategy on technology. If you are in a position to promote digital transformation in your organization, then please read on.

This article will cover:
o What are some examples of digital transformation in manufacturing?
o Why should companies implement digital transformation?
o Where should companies start?
Examples of Digital Transformation in Manufacturing
There are six key aspects of digital transformation as they relate to manufacturing. These are:
1. Automation & Digitalization
2. 3D Printing
3. The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) and Smart Sensors
4. Augmented Reality (AR)
5. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (AI/ML)
6. Analytics and Automated Business Processes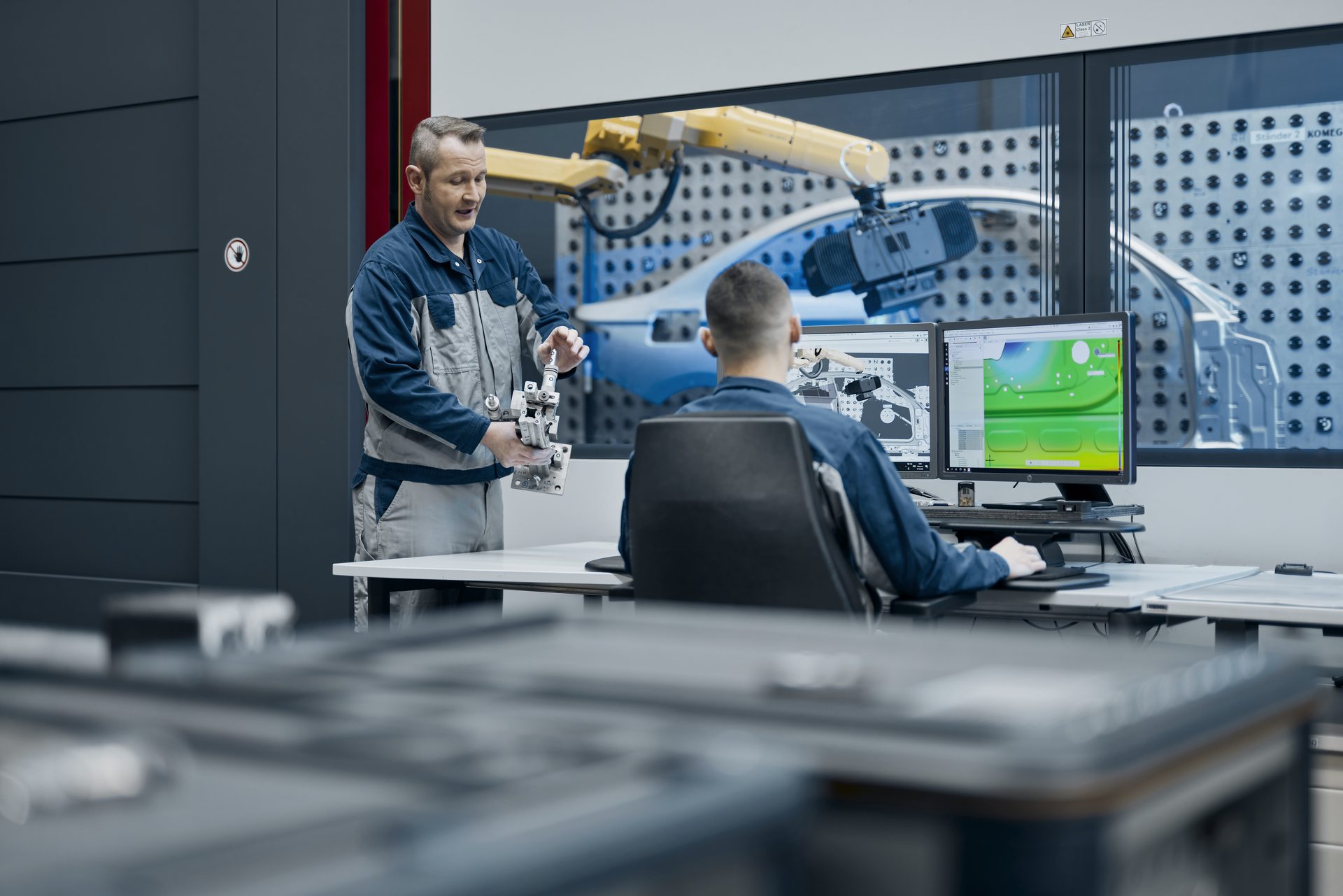
1. Automation and Digitization
Manufacturers are constantly striving to gain better control of their processes and understand the strengths and weaknesses of their products. Advanced automation techniques for each manufacturing stage, including inspection and production, are at the forefront of digital transformation.
The use of digitalization to move from 2D to 3D representations greatly impacts the amount of data a business can capture about what it does. Digital automated inspection gives greater insights, process control and feedback on the finished product, supporting agile manufacturing.
Many businesses are moving from manual inspection to automated inspection processes. This shift reduces human error, increases throughput, and, subsequently, data capture, and frees-up staff from repetitive processes to focus on more complex contributions.
2. 3D Printing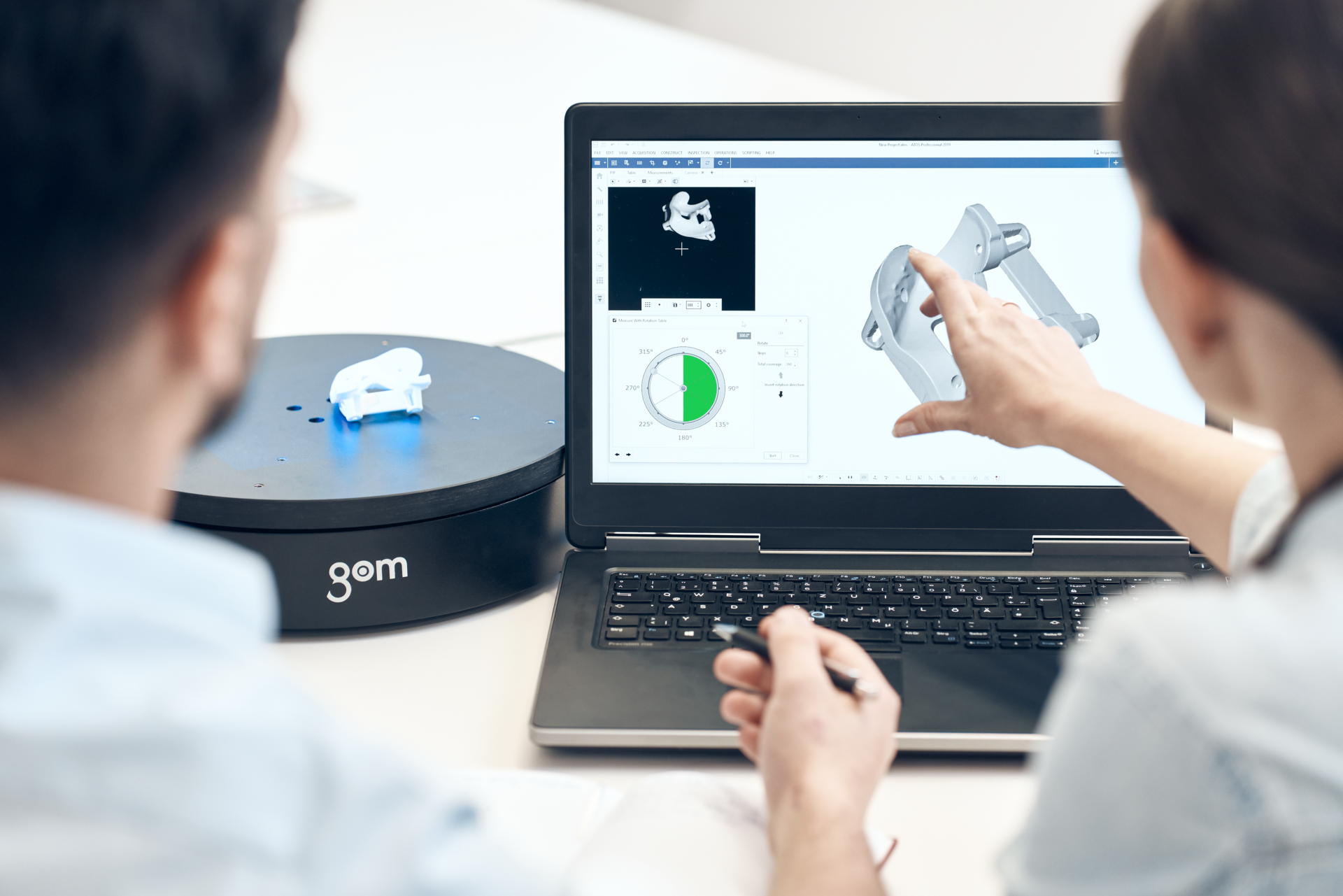 3D printing allows manufacturers to create low-cost product prototypes quickly, dramatically reducing the lead time of bringing parts and products to market. 3D printing processes can produce complex geometries previously unattainable by traditional manufacturing methods. With this advancement, product designers are no longer limited to what can be produced through traditional machining methods. 3D printing quality and precision have made additive manufacturing a viable industrial production.
3D printing allows manufacturers to create low-cost product prototypes quickly, dramatically reducing the lead time of bringing parts and products to market. 3D printing processes can produce complex geometries previously unattainable by traditional manufacturing methods. With this advancement, product designers are no longer limited to what can be produced through traditional machining methods. 3D printing quality and precision have made additive manufacturing a viable industrial production.
Digital automated inspection is the perfect companion to 3D printing, which has proven itself a critical tool for problem-solving issues in manufacturing environments and process development labs.
Detailed 3D models, or digital twins, and reverse engineering from 3D scan data can shorten analysis times for research and development (R&D) teams or support competitor analysis.
3. Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) and Smart Sensors
The rapid spread of devices that capture and analyze data has significantly changed the traditional production environment over the last few years.
The connectivity between production machines and automated inspection equipment now means that defects and variations on manufacturing lines can be trended and analyzed in real time. Adverse trends from incoming materials, process variations, and manufacturing condition shifts can be identified and addressed immediately with targeted actions.
Automated inspections can trigger earlier interventions upstream in the manufacturing process to avoid mistakes before costly scrap is produced.
Connected devices and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) allow different devices to communicate effectively to create a coherent, connected manufacturing assembly line.
4. Augmented Reality (AR)
Augmented Reality (AR) is poised to become one of the most disruptive technologies of our time as computer processing power and the quality of graphic visualizations improve over the next two to three years.
As headsets become lighter and smaller, the factory of the future is likely to include AR for applications such as:
• Viewing instructions “hand-free” while completing maintenance on equipment
• Viewing exploded views of complex assemblies suspended and manipulated in mid-air
• Customer and stakeholder demonstrations of new products, area layouts, and experiences
• Quality control comparisons of a physical component versus an accurate digital twin
• Reliable manufacturing simulations derived from 3D scan data from a metrology-grade 3D scanner to evaluate form, fit and function
5. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (AI/ML)
While the use of AI is becoming widespread, the impact on production equipment in manufacturing is likely to be just as profound.
Equipment that can independently identify process variation, adjust the machine’s settings and configuration, and bring the output back to the ideal specification will likely transform manufacturing support as we know it.
Inspection equipment that can learn and self-teach through exposure to new defects means that quality control measures can improve with time as the equipment gains more experience in real-world situations.
6. Analytics and Automated Business Processes
Digital transformation in manufacturing applies not only to the production of components but to the management and administrative side of the business.
Many world-leading manufacturers are using digital transformation to integrate their business processes, so that customer orders flow through production in a modern, seamless way:
• Customer orders are received online or electronically
• Automated systems then schedule production (including management of inventory levels and the ordering of materials if required)
• Orders are tracked through production, inspection and quality control, with digital records for each batch leaving a detailed audit trail
• Labelling, packaging, shipping and fulfillment of orders are carried out automatically, with the products and quantities reconciled with the orders received
• Customers receive tracking updates and invoices using integrated accounting software
These process steps can be completed using semi-autonomous systems, which will optimize over time for your key performance parameters without ever needing intervention from staff.
Custom orders can be accepted, and with added agility from flexible, automated systems, each customer can receive a digital twin of the component, providing a detailed digital representation for future analysis.
Why Should Manufacturers Implement Digital Transformation?
There are a host of benefits to implementing digital transformation in manufacturing, including:
1. Improved Efficiency
Digital transformation enables manufacturers to optimize their operations and improve efficiency. Manufacturers can streamline procedures and improve production outputs by leveraging technologies such as robotics, automated digital inspection, and smart sensors. Routine tasks can be automated, allowing workers to focus on more complex or strategic activities. With the implementation of digital transformation technologies, manufacturers can also monitor and track their operations in real-time, allowing them to identify further potential improvements.
Through the use of connected technologies, intelligent predictive maintenance routines can be developed. Based on the status and health of the equipment, maintenance can be scheduled before costly downtime occurs (and scheduled during planned downtime) rather than lost production hours. Furthermore, predictive maintenance can help optimize equipment usage and reduce the risk of equipment failure, improving overall efficiency.
Digital transformation can also help manufacturers reduce costs associated with manual or paper-based processes. Manufacturers can reduce errors, speed up processing times, and improve accuracy by digitizing manual processes.
2. Reduced Scrap and “Hidden Factory” Costs
Digital transformation encourages advanced forms of lean manufacturing. Automated 3D scanning equipment can generate vast amounts of production data very quickly. The data can be collected and analyzed, revealing real-time trends and allowing production and quality control teams to react to upstream problems before parts are manufactured out-of-specification.
Soon processing equipment will be able to react to triggers from automated inspection, assess the condition of its processes and self-adjust settings to compensate for incoming variation.
Through the use of reliable data throughout the modern digital factory, the identification and elimination of waste in the “hidden factory” can be achieved more easily. Rework costs for scrap components, time wasted by checking and re-checking in manual processes, and automated inventory management levels can all contribute to a reduction in not only yield metrics but also the Overall Cost of Goods (O-COGS) for a product.
3. Ability to Quickly Adopt New Technologies
Digital transformation allows manufacturers to be more adaptable, making it easier to adopt new technologies. By creating a culture of innovation, manufacturers can leverage digital technologies to experiment with new products, services, and business processes. Digital transformation enables manufacturers to be more flexible and adaptive, allowing them to stay ahead of the competition and respond to changing market needs. Manufacturers can swiftly improve their operations by implementing cutting-edge technologies, empowering them to penetrate new markets and create new revenue streams.
AI and IIoT are rapidly changing the manufacturing landscape, enabling manufacturers to collect and analyze vast amounts of data from sensors and other sources. By embracing emerging technologies, manufacturers can gain valuable insights into their operations, customers, and markets, enabling them to make informed decisions and stay ahead of the competition.
4. Become More Agile with Improved Decision-Making
Digital transformation allows manufacturers to access reliable data in real time, enabling them to make better-informed decisions. Manufacturers can gain valuable insights into their operations, customers, and markets by collecting and analyzing data from multiple sources.
Data-based decision-making fosters an atmosphere of trust and transparency within an organization. Collating data into a “single source of truth” (for example, an enterprise-level production or quality metric, such as MBD/PMI) gives all teams in operation a clear, focused goal. Using objective information from trusted automated sources reduces the risk of conflict between teams and departments.
5. Identify Trends, Weaknesses, and Bottlenecks
Digital transformation can help manufacturers identify weaknesses and bottlenecks across the entire organization. Manufacturers can identify areas for improvement and make informed decisions to optimize their supply chains by collecting and analyzing data on supplier performance, delivery times, and quality.
Smart factory production systems bring greater clarity to Work-in-Progress (WIP) and inventory management levels, allowing greater analysis of complex production flows. Workflow leveling and removing bottlenecks in production can be achieved easily once this vital data is collected and made available for analysis.
6. Break Down Silos
Digital transformation can help break down silos between different departments and functions within a manufacturing organization. By creating a unified platform for data sharing and communication, manufacturers can improve collaboration and eliminate information silos.

Manufacturers can provide real-time data to all stakeholders by implementing a centralized data repository, enabling them to make informed decisions and improve overall effectiveness.
Furthermore, digital transformation in manufacturing can help break down silos both upstream and downstream. Sharing objective data between teams enhances communication and improves supplier, distributor, and customer collaboration. This improved communication helps reduce lead times, optimize supply chains, and improve overall customer satisfaction. By breaking down silos within a supply chain, manufacturers can create a more agile and responsive unit that is better equipped to respond to ever-changing market conditions.
How to Start a Digital Transformation in Manufacturing
Utilizing a metrology-grade 3D scanner is a simple yet effective way to begin a digital transformation journey in manufacturing. Professional 3D scanners collect accurate data that reveals quality issues, optimizes processes, helps to improve product quality and supports lean manufacturing.
By visualizing results using 3D metrology software, manufacturers can leverage digital transformation to improve communication and support collaboration throughout the organization and with external business partners.
Replacing traditional inspection techniques with digital 3D scanning is a fast method of building a database of vital production data for:
• Root-cause analysis of defects
• Identifying opportunities for product improvement
• Helping to eliminate waste and improve operational productivity
Digital transformation in manufacturing is constantly evolving. Understanding how to implement it now will help your business in the future. Watch our webinar about digital transformation in manufacturing.







